Pain is something nearly everyone experiences—whether it’s occasional muscle soreness, migraines, or the persistent aches of arthritis. While medications can provide fast relief, they often come with side effects or the risk of dependency when used long-term.
The good news? Science increasingly shows that what you eat can play a significant role in how your body manages pain. By choosing the right foods, you can help lower inflammation, reduce discomfort, and support your body’s natural healing processes.
In this guide, we’ll explore how dietary changes serve as natural pain remedies, highlight foods with proven benefits, and share practical strategies to make your meals part of your pain-management toolkit.
Understanding Chronic Pain
Chronic pain is more than just an ongoing ache—it’s often a signal of underlying inflammation or nerve dysfunction. Conditions like:
- Arthritis – Joint inflammation causing stiffness and pain.
- Fibromyalgia – Widespread musculoskeletal pain linked with fatigue and mood issues.
- Migraines – Severe headaches often triggered by diet, stress, or hormonal changes.
- Neuropathy – Nerve damage that causes burning, tingling, or sharp pain.
While each condition is unique, inflammation is a common denominator. Unhealthy eating habits—high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats—can worsen this inflammation. Conversely, a nutrient-rich diet can calm the body’s inflammatory response.
How Food Affects Pain
Food is more than fuel—it’s information for your body. Certain nutrients switch inflammation “on” or “off.” For example:
- Omega-3 fatty acids → Reduce inflammation by lowering cytokine activity.
- Antioxidants → Protect cells from oxidative stress, which contributes to pain.
- Polyphenols → Plant compounds that regulate inflammation and improve circulation.
On the flip side, processed foods, refined sugars, and trans fats act like fuel on the fire, making pain symptoms worse.
📖 Further Reading: Harvard Health: The Inflammation Connection

Also Read: Which Natural Supplements Help Ease Muscle Soreness?
Best Anti-Inflammatory Foods for Pain Relief
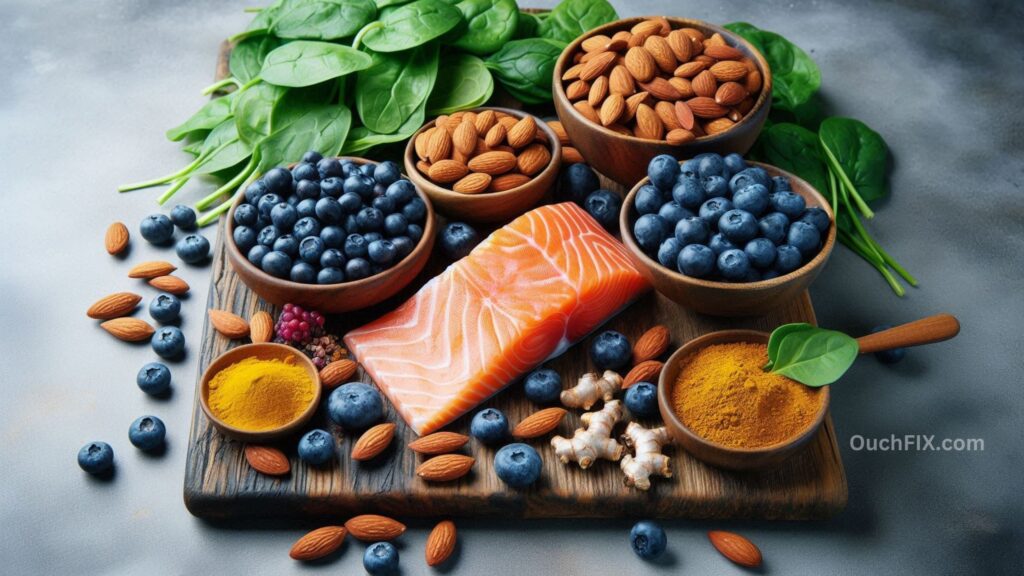

1. Fatty Fish and Omega-3s
Salmon, sardines, and mackerel are rich in omega-3s, which reduce joint tenderness and stiffness. Studies show that omega-3s can be as effective as NSAIDs (like ibuprofen) in reducing arthritis symptoms.
Tip: Aim for two servings of fatty fish per week, or consider a high-quality fish oil supplement after consulting your doctor.
2. Leafy Greens and Antioxidants
Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are loaded with vitamins C, E, and K—powerful antioxidants that shield cells from damage and reduce inflammatory markers.
Example: People who follow plant-forward diets rich in leafy greens often report reduced stiffness and improved mobility in arthritis research studies.
3. Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are packed with healthy fats, magnesium, and fiber. Magnesium, in particular, plays a role in muscle relaxation and nerve function, making it crucial for pain relief.
4. Berries and Polyphenols
Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are high in polyphenols like anthocyanins. These compounds reduce oxidative stress and may ease joint pain.
Fun Fact: A study from the Journal of Nutrition found that people who ate berries daily had significantly lower levels of C-reactive protein, a key marker of inflammation.

Also Read: What are Safe Natural Remedies for Arthritis Pain?
Herbs and Spices That Work Like Natural Painkillers
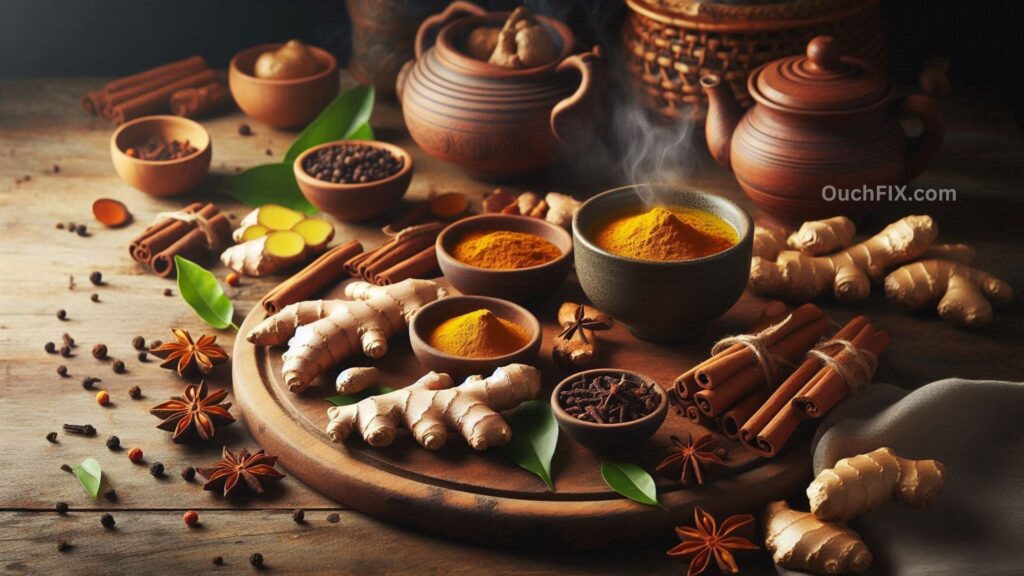

Turmeric and Curcumin
Curcumin—the active compound in turmeric—is one of the most studied natural anti-inflammatories. It has been shown to reduce pain levels in people with osteoarthritis, sometimes rivaling prescription drugs.
Tip: Pair turmeric with black pepper to increase absorption.
Ginger’s Pain-Relieving Power
Ginger contains gingerol, a compound with analgesic (pain-relieving) properties. It has been shown to help with muscle soreness after exercise and reduce menstrual pain.
Cloves and Eugenol
Cloves contain eugenol, which has mild anesthetic properties. For centuries, clove oil has been used to ease toothaches and headaches naturally.
Other Key Factors in Pain Management

Staying Hydrated
Even mild dehydration can cause muscle cramps and joint stiffness. Drinking enough water, herbal teas, and electrolyte-rich drinks can help keep your body functioning smoothly.
Gut Health and Pain
The gut and brain are deeply connected. An unhealthy gut microbiome can fuel systemic inflammation. Including probiotic-rich foods like:
- Yogurt
- Kefir
- Sauerkraut
- Kimchi
…can support both digestion and pain management.
Foods That Make Pain Worse
Certain foods can worsen pain symptoms. Common culprits include:
- Processed meats (sausage, hot dogs)
- Sugary drinks and refined carbs
- Artificial additives and preservatives
- Excessive alcohol
Cutting back on these can dramatically improve how you feel day-to-day.
A Balanced Diet for Pain Relief
An anti-inflammatory diet doesn’t need to be restrictive—it’s about balance and variety. Key components include:
- Complex carbs: Provide steady energy (brown rice, quinoa, oats).
- Protein: Supports tissue repair (lean meats, beans, tofu).
- Healthy fats: Reduce inflammation (olive oil, avocado).
Key Nutrients for Pain Management
Deficiencies in certain vitamins and minerals can worsen pain. Make sure you’re getting enough of:
- B Vitamins → Aid in nerve health and energy production.
- Magnesium → Supports muscle and nerve function.
- Vitamin D → Low levels are linked to chronic pain and bone weakness.

Also Read: How can I Relieve Joint Pain at Home with Natural Ingredients?
Diet Plans That Help Reduce Pain

The Mediterranean Diet
This eating style emphasizes whole grains, fresh produce, fish, nuts, and olive oil. Research consistently links it with lower inflammation and reduced risk of chronic disease.
Intermittent Fasting
Fasting cycles may lower inflammation and encourage cellular repair. Some studies show benefits for people with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
⚠️ Note: Intermittent fasting isn’t suitable for everyone—especially those with diabetes, eating disorders, or certain medical conditions. Always check with a healthcare professional before starting.
Beyond Diet: Other Lifestyle Changes for Pain Relief
While diet is powerful, it’s not the only piece of the puzzle. Additional strategies include:
- Stress management: Chronic stress amplifies pain perception. Practices like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can help.
- Regular exercise: Strengthens muscles and reduces stiffness.
- Quality sleep: Restorative sleep lowers inflammation.
Q1. Can diet really replace pain medication?
Not entirely. Diet can reduce inflammation and ease pain, but it may work best when combined with medical treatments. Always follow your doctor’s advice.
Q2. How long does it take for dietary changes to affect pain?
Some people notice improvements within weeks, while others may need several months of consistent changes.
Q3. Are supplements as effective as whole foods?
Whole foods are generally better, but supplements (like fish oil or turmeric capsules) can be useful for people with specific deficiencies.
Q4. Is coffee good or bad for pain?
Coffee can reduce headache symptoms in small amounts, but too much caffeine may trigger migraines or increase inflammation.
Q5. Can a plant-based diet help with chronic pain?
Yes. Plant-based diets are naturally rich in anti-inflammatory compounds, though it’s important to ensure adequate protein and vitamin B12 intake.




